Take a quick scroll through social media, and amazon revealing several supplements “claiming” to build muscle and strength. For years they have been very popular, but popularity does not always equate to efficacy. So, the questions remain, do any of this work and are backed by science? This article discusses supplements that help build muscle and strength based on the research.
Supplements that have enough studies to prove effective
Some supplements have been proven after extensive research to help build muscle strength. Here are some of them and how they work:
1.Creatine
The International Society for Sports Nutrition (ISSN) has described creatine as “the most effective supplement available to athletes to increase high-intensity exercise capacity and muscle mass during training. “Creatine itself is a molecule that naturally occurs in the body. However, the supplementation may increase the creatine content in the body by up to 40%.
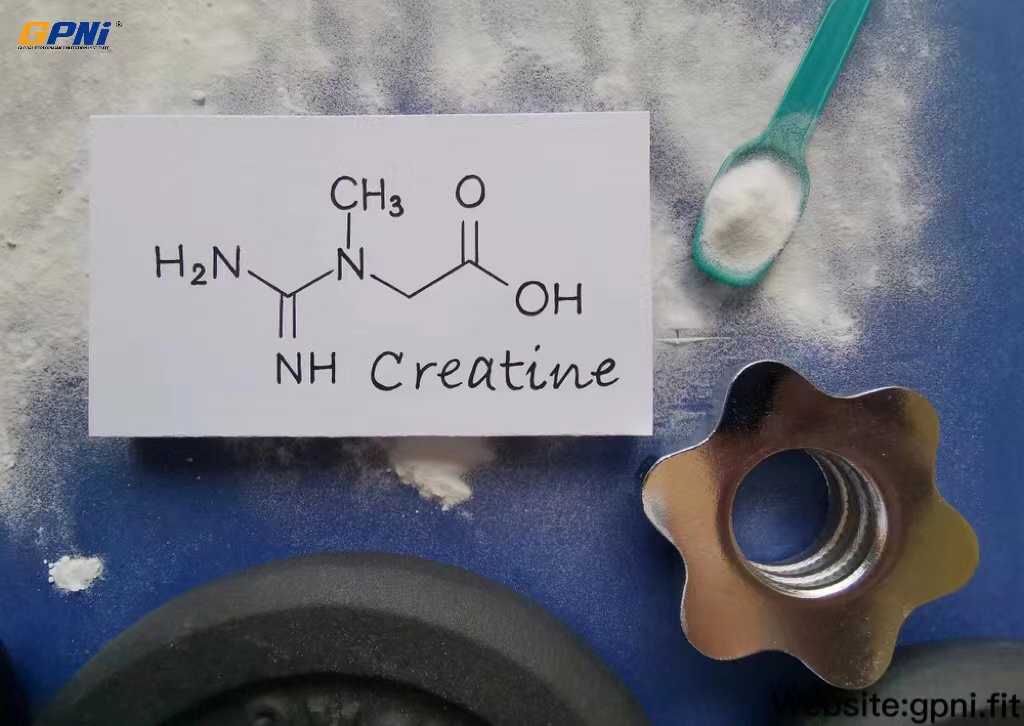
Several studies have shown that taking creatine supplements increase muscle concentration and strength. For example, a review reported by the National Centre of Biotechnology Information (NCBI) revealed that creatine improved lower limb strength. This review considered about 60 studies.

Read full details on the study here: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25946994/.
Another review of 53 studies revealed that creatine supplementation was effective for upper limb strength.
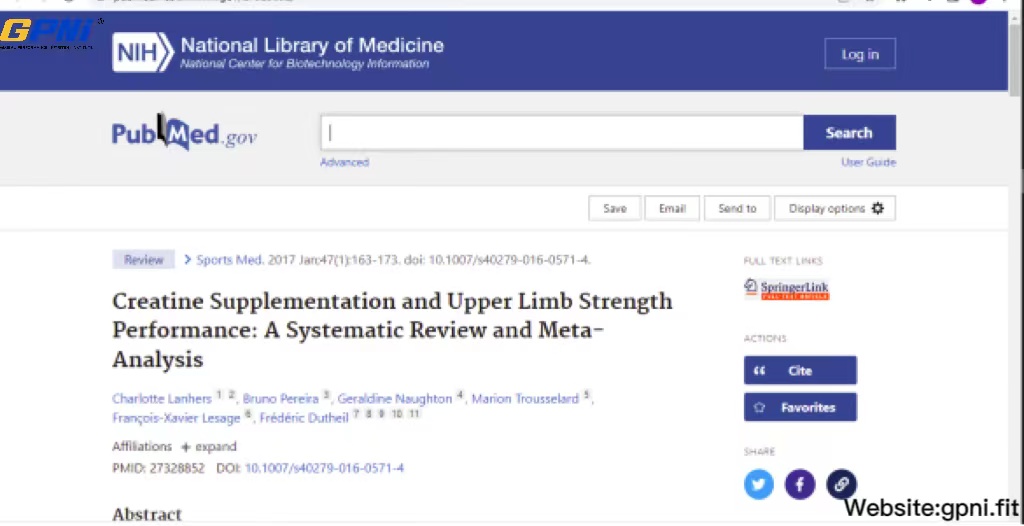
According to the ISSN, the only clinically significant side effect of taking creatine supplements has been weight gain. In addition, it noted that recent studies had found no harmful effects of creatine supplementation and noted that creatine may lessen the risk of injury during training. The research concluded that supplementing the diet with creatine or creatine-containing formulations could provide safe and effective methods of increasing muscle mass and strength.
2.Protein Supplements
Protein is essential for building muscles. Generally, your body may need to consume more protein than it breaks down to build muscles. Taking food rich in protein may already help the body get all the protein it needs to build muscles and strength. However, studies reveal that protein supplements may be helpful in building muscle and strength in those who lack enough in their daily diet.

One study concluded that taking whey protein supplements was more effective at causing muscle gain than adding carbs. According to researchers, “In comparison to carbohydrates or other non-whey protein supplements, whey protein alone or in combination with other ingredients seems to maximize lean body mass gain, as well as upper and lower body strength gains. When consumed along with creatine, whey protein seems to possess the most potent effect..”
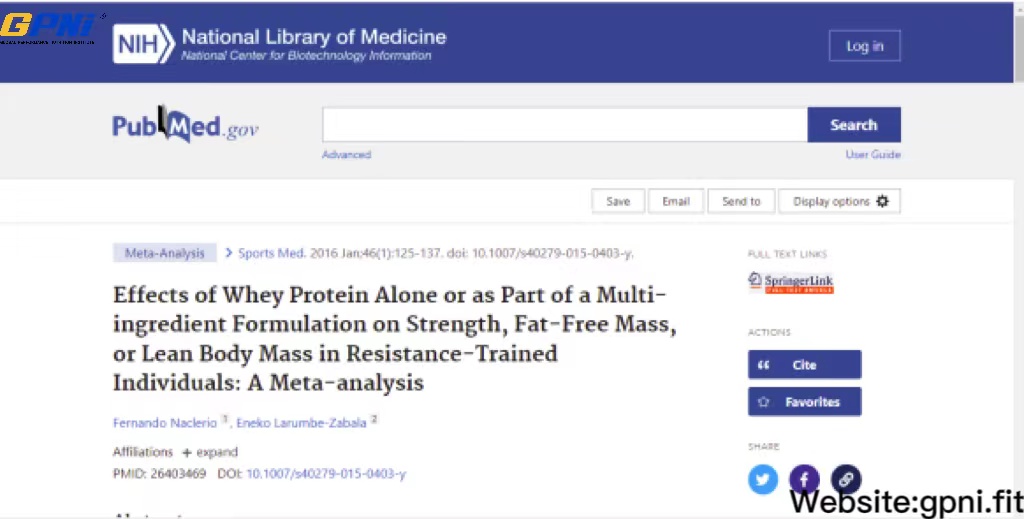
Read full details of that study here: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26403469/.
Another study that sought to see the effect of whey protein supplementation on muscle composition, strength, and endurance during 10-weeks of resistance training concluded that whey protein supplementation did cause an increase in fat-free mass.
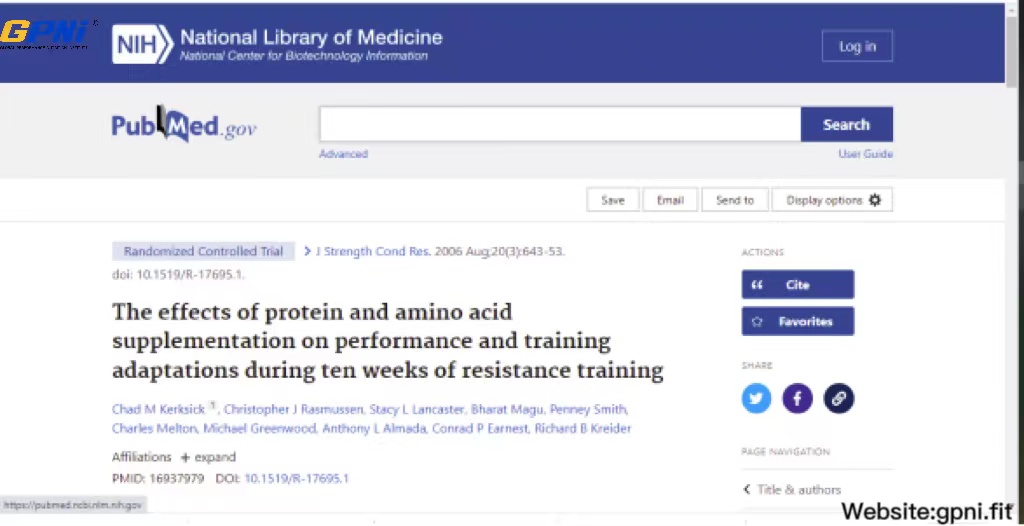
Read detail of the study here: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16937979/
Popular examples of protein supplements are whey, pea, soy, and casein protein. It is also important to note that studies reveal that protein supplements help build muscles and strength in individuals with low protein but have minimal or no effect in individuals who are already taking sufficient protein.
3.β-hydroxy β-methylbutyrate
The ISSN has categorized HMB as an “apparently effective” supplement that may typically increase muscle mass and strength, especially among untrained individuals. HMB is made when leucine, a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA), is broken down by the body. However, because the body produces it in small amounts, many take HMB supplements to increase its levels in the body.
Researchers tested HMB supplementation and its effect on untrained individuals’ muscle strength and mass in two studies involving 41 and 28 participants. The conclusion of the studies published by the NCBI stated that supplementation with either 1.5 or 3 g HMB/day could result in more significant gains in muscle function associated with resistance training.

Read full details of the study here: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8941534/.
Another study conducted on 39 men and 36 women revealed that regardless of gender or training status, HMB may increase upper body strength and minimize muscle damage when combined with an exercise program.
Read full details here: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10978853/.
However, it is essential to note that some other studies have shown a minimal, or no effect of HMB on muscle gain and strength when applied to athletes. Therefore, concluding on the effectiveness of HMB, the ISSN stated there was some evidence that HMB enhances training adaptations in individuals just starting. It went on to state that HMB may enhance training adaptations in athletes, but further research is needed to establish this fact.
Supplements that claim to be effective but have no studies to prove it
While there are supplements that have science to prove their effectiveness or at least their effectiveness in certain situations. Many have great marketing but offer little no studies are yet to conclusively prove their effectiveness.
Here are some of them:
1.Conjugated Linoleic Acids
The ISSN has classified CLA under ineffective supplements. Already, research is conclusive that as a fat-loss supplement, CLA may not be a miracle worker, with many studies and reviews showing a minimal or low effect on fat loss. One such review stated the impact of CLA on fat loss; thus: “CLA has minor effects.” “The clinical relevance remains unknown.” “The evidence suggests that CLA consumption does not lead to clinically relevant changes in body composition over time.”
Read full details here: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10531600/.
As for the effects of CLA on muscle gain and strength, or even fat loss, the ISSN said that although animal studies suggest adding it to dietary feed increases both muscle and bone mass, most studies conducted on humans have shown little to no effect on body composition or muscle growth.
2.Ornithine-α-ketoglutarate (OKG)
The ISSN classifies this supplement as “too early to tell,” which means that further studies will have to be conducted to conclude its effect on strength and muscle gain. Studies already conducted on animals show that OKG may theoretically be valuable to athletes involved in intense training because it may improve protein balance. In fact, a study revealed that OKG supplementation during 6-weeks resistance training caused more gain in bench press. However, no significant differences were seen in squat strength, training volume, and muscle mass gains. All these only emphasize the need for more research on OKG.

Conclusion
The effectiveness of supplements can be measured by scientific evidence, and individuals must consider this before opting for them. The ISSN has a comprehensive ranking on some supplements, and you can view the ranking here: https://jissn.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1550-2783-1-1-1.

To know more about supplements and their effectiveness, get learning resources such as those listed below, and register today to be a Sports Nutrition Specialist (SNS®) on the GPNi® platform.
You also learn about the GPNi®’s patented “traffic light system.”
● Green – Good & Solid Research
● Orange – Some Limited Research but Not Considered Harmful
● Red – No Solid Research and Maybe Some Health Concerns
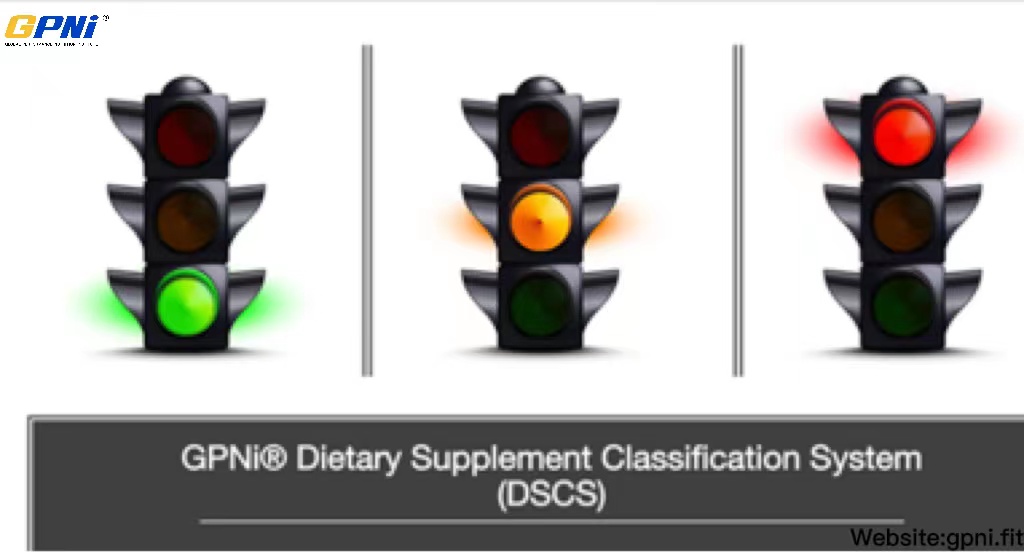
This enables you to learn what to safely recommend to your clients, athletes, and yourself.
Take your sports nutrition knowledge to the next level and qualifications by getting studying and getting certified with the GPNi®. GPNi® is the official partner of the ISSN globally online and offers the official and exclusive courses to help prepare you to pass the official ISSN certifications, The Sports Nutrition Specialist (SNS, and the Certified Sports Nutritionist (CISSN).
Here are a list of all the GPNi® certificate and certification programs.
International Certifications Available In 2022
Continued Education Certificates In 2022
For more information please check out this page: https://thegpni.com/education/certifications-courses








