The Keto diet is a type of diet that promises to reduce body fat, improve health and provide mental clarity. While it is true that the ketogenic diet can be beneficial to the body, not all keto diet claims can scientifically proven. This article details some myths about the famous keto diet and what would be wise to avoid.
What is a Ketogenic Diet?
A ketogenic diet is a style of eating characterized by a very low carb intake and high fa intake. It shares many similarities with low carb and Atkins diets.
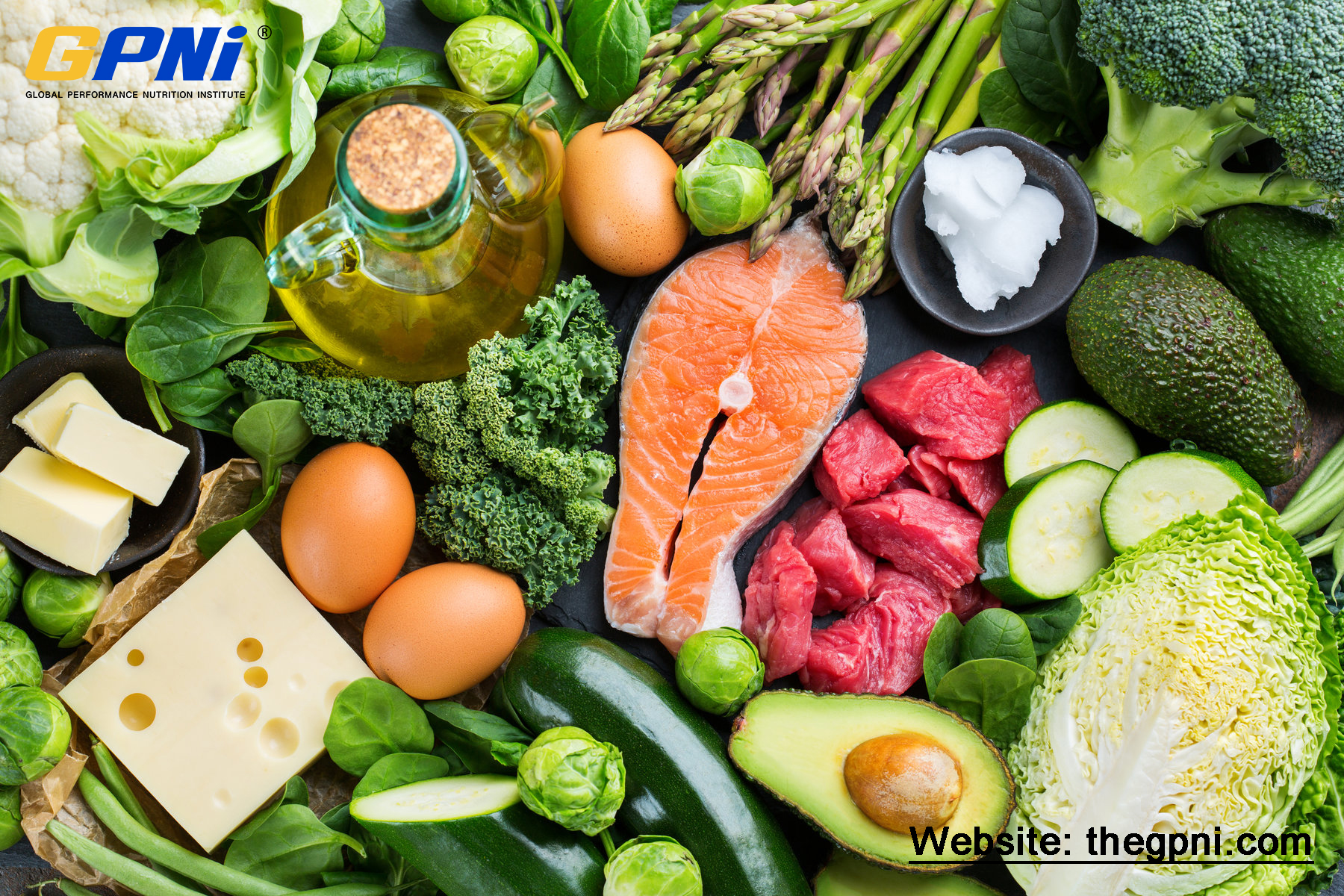

The diet replaces carbohydrates with fat by drastically reducing carbohydrate intake. In the process of reducing carbs, the body enters a metabolic state called “ketosis.” Ketosis refers to a process where the body uses ketones instead of carbs for fuel. Ketones are made from fatty acids in the liver. Therefore the body burns fat for energy with incredible efficiency. Ketones can supply energy for the brain.
A ketogenic diet can have significant effects on blood sugar and insulin levels, which may possess health benefits for the body alongside the increased ketones.
Brief History and Origin of the Keto Diet
In 1921, Dr. Russell Wilder from Mayo Clinic created the ketogenic diet ( even though its idea had existed long before then). The diet was used to treat children with intractable pediatric epilepsy.

He noticed that some of his epileptic patients had fewer seizures when their sugar level was low. This low blood sugar level was caused by a diet high in fat and low in carbohydrates. Thus, the ketogenic diet was used as a therapeutic diet for pediatric epilepsy for almost a decade. After the introduction of antiepileptic drugs, the ketogenic diet’s popularity waned.
Types of Keto Diet
There are several variations of the keto diet, and they include:
Standard ketogenic diet (SKD): It is sometimes referred to as the true keto diet. This diet consists of very low carbs, moderate protein, and high fat. Typically, 70% of the calories come from fat, 20% protein, and 10% carbohydrates.
Targeted ketogenic diet (TKD): This diet allows for carbs before or after workouts. This is to ensure that individuals have enough energy during exercise.
Cyclical ketogenic diet (CKD): In this diet, individuals consume more carbohydrates after a period of low carbs, such as following a standard keto diet for four days and then eating carbs for two days. It is also referred to as carb backloading or the cycle keto diet.
High protein ketogenic diet: This diet has more protein than a typical ketogenic diet. About 60 percent of it is fat, 35 percent is protein, and five percent is carbohydrates.
Calorie-Restricted Ketogenic Diet: A calorie-restricted ketogenic diet is similar to a standard ketogenic diet. There is one main difference between the two: the number of calories is set in a calorie-restricted ketogenic diet.
Keto Diet Myths
There are a lot of concepts and beliefs about the Keto diet are true but also various aspects, which are simply myths. Some of them are discussed below.
Keto Diets Affect Strength Performance in Athletes ( Gymnasts)
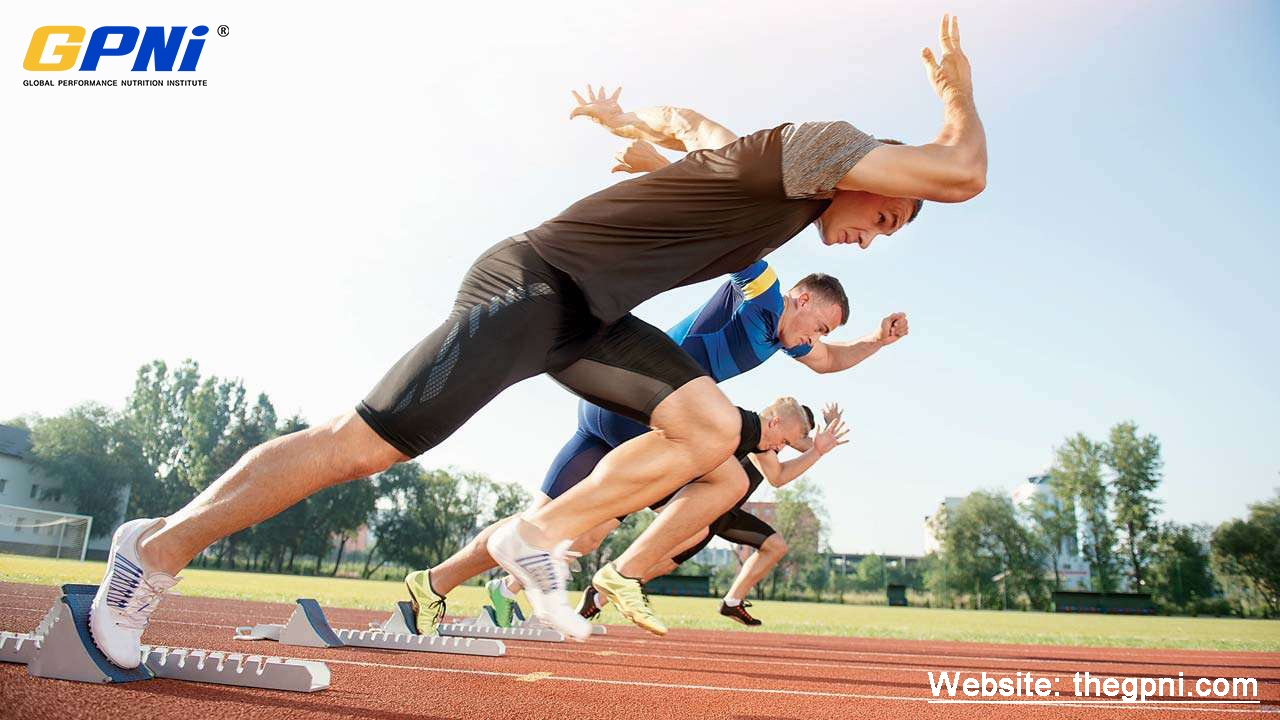

Coaches and doctors have shown concern over the years about the negative effect of the keto diet on athletic performance, especially as it relates to strength performance. However, studies published by the Journal of International Society for Sports Nutrition suggest that very low carbohydrate ketogenic diets do not negatively impact strength.
A study involving eight athletes, elite artistic gymnasts (age 20.9 -55.5 years), looked at the effects of a very low carbohydrate keto diet on strength. Study results revealed that following a keto diet for a relatively short period (i.e., 30 days). reduced body weight and body fat without negatively impacting strength performance.
Read full details of the Study here
2. Carbohydrate Requirements Are The Same for Everyone

It is yet another myth about Keto diets that carbs will be the same for everyone. Truth be told, the carb requirements for each individual vary for various reasons, including health.
As one begins a very low-carb diet like keto, the typical carb intake is about 20 to 50 grams (g) of carbohydrates each day. Individuals usually start at the lower end of that range to help the body enter ketosis. Other individuals may eat a higher number of carbs depending on factors like physical activity. Therefore, experts recommend partnering with a dietitian who can determine nutritional requirements..
3. You Can’t Eat Fruits and Veggies While On a Keto Diet.

Fruits and veggies contain carbohydrates. However, this doesn’t mean they should be completely avoided. The reason is that these unprocessed whole foods are rich in vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber need to be included in the diet. Fiber, in particular, is key to preventing constipation, a side effect that is common to keto dieters. Despite this, it should be noted that some very healthy foods are still not permitted when following a keto diet. For example, swapping junk food in a diet for high-carb, ripe bananas would improve health. However, bananas may be not be permitted on the keto-diet because of their high carbohydrate content.
4. The Keto Diet is the Best Way to Lose Weight by Diet

Another myth is the belief that the Keto diet is the best way to lose weight for every individual. However, experts have reiterated that differences between people impact an individual’s rsponse to a diet. Contraty to popular belief, the Keto diet is not the only or the diet for weight loss The results of research published in the online journal named Cell showed that people respond differently to the same foods in terms of blood sugar. This demonstrates that diets are not a one-size fits all approach.
Read full Details here
Indeed, the best diet will be one that an individual can be consistent with and agrees with the individual’s genes and personal health.
5. Eating Carbs Causes Diseases
Another major myth that leads many into the keto diet is the idea that eating carbs always causes diseases. However, healthy individuals can eat plenty of carbs without harm if they opt for whole foods.
Health Benefits of the Keto Diet
The keto diet has been proven to possess the following health benefits.
1. It helps to reduce weight.

You can lose weight and reduce the risk of disease by following a ketogenic diet. Keto diets may be just as effective as low-fat diets for weight loss, according to new research. In a review of 13 studies published by the British Journal of Nutrition, a low-carb, ketogenic diet was found to be slightly more effective than a low-fat diet in terms of weight loss.
Read full Details here
Furthermore, the Journal of Nutrition Metabolism published a study investiagting the effects of the ketogenic diet. 34 older adults following a ketogenic diet for eight weeks, lost three times as much fat as those following a low-fat diet.
To Read Full Details
2. It aids with diabetes.
Losing excess fat can help prevent type 2 diabetes, pre-diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Study results from the Journal of Diabetes Resaerch reported women with type 2 diabetes following a ketogenic diet for 90 days helped reduce hemoglobin A1C, a measure of long-term blood sugar control.
To Read Full Details, Click Here:
A study followed subjects for 2-years. The results showed that people following a ketogenic diet lost an average of 26.2 pounds (11.9 kg). Since weight is linked to type 2 diabetes, this is an important benefit to consider.
Read full Details here
Other Health Benefits Include:
- Children with epilepsy on the ketogenic diet have significantly fewer seizures
-
Alzheimer's disease symptoms may be reduced, and the disease's progression slowed by following a ketogenic diet
Conclusion
The keto diet can be beneficial to health in many ways. Other benefits are even being still being explored. Yet for all the good, it is essential to distinguish truth from myth, like the belief that it is the best diet for everybody on earth trying to lose weight.
To know more about the scientific truth of Keto diets, get more learning resources such as those listed below, and get registered today to be a Sports Nutrition Specialist (SNS®) on the GPNi® platform.

You can also choose one of our Continued Education Certificate programs, such as the Endurance & Marathon Nutrition Coach (EMNC®) certificate program.
References
https://jissn.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1550-2783-7-7
https://jissn.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1550-2783-9-34
https://jissn.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12970-021-00459-9
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6251269/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28639757/
https://www.everydayhealth.com/ketogenic-diet/diet/keto-diet-myths-you-shouldnt-believe/
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-myths-within-the-low-carb-community
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/9-weight-loss-diets-reviewed https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/fruit-and-low-carb







